Unleashing the Beast: A Comprehensive Guide to Modifying Naturally Aspirated Engines
For many automotive enthusiasts, the allure of a naturally aspirated (NA) engine is undeniable. It offers a raw, responsive, and linear power delivery that’s hard to replicate with forced induction. While turbocharging and supercharging can dramatically increase power, modifying an NA engine provides a unique sense of accomplishment and can unlock hidden potential. This guide will walk you through the most effective modifications for enhancing the performance of your NA engine.
Understanding the Fundamentals
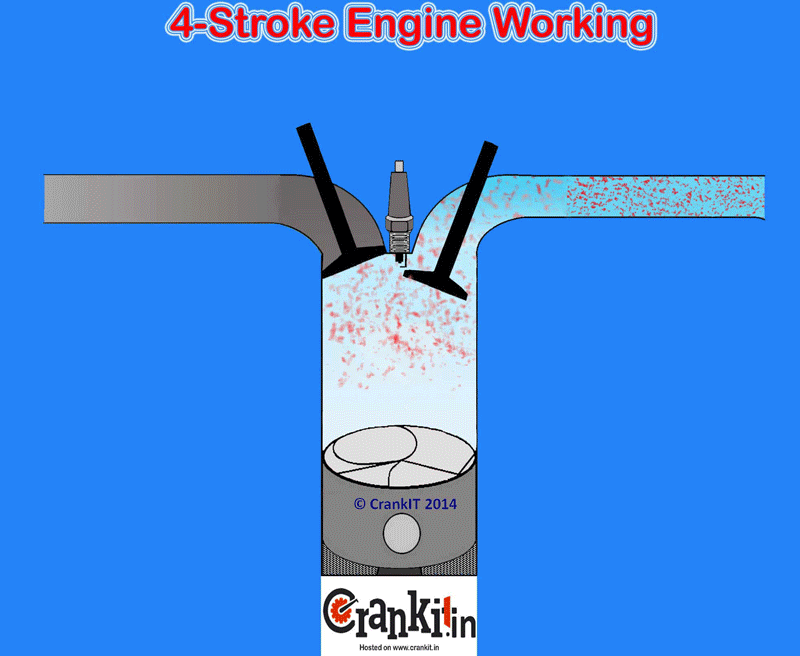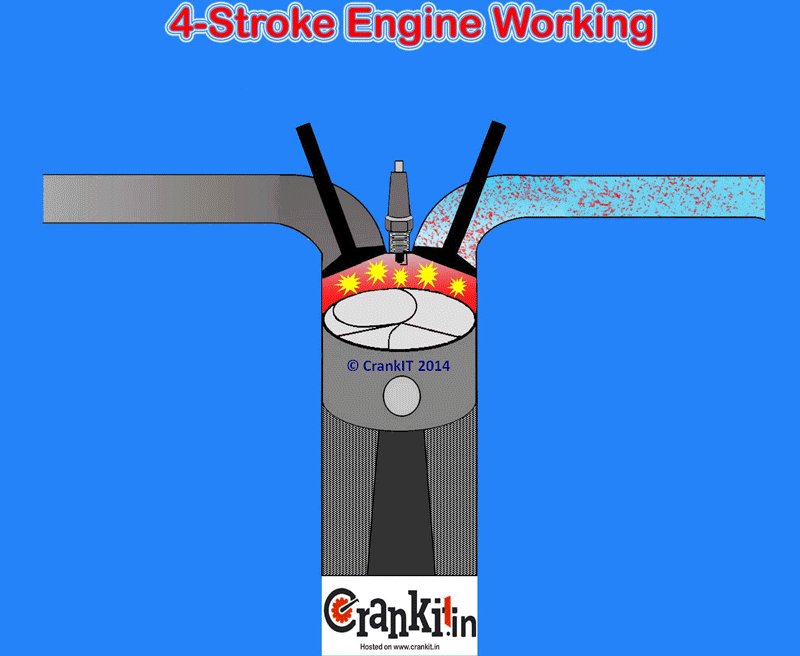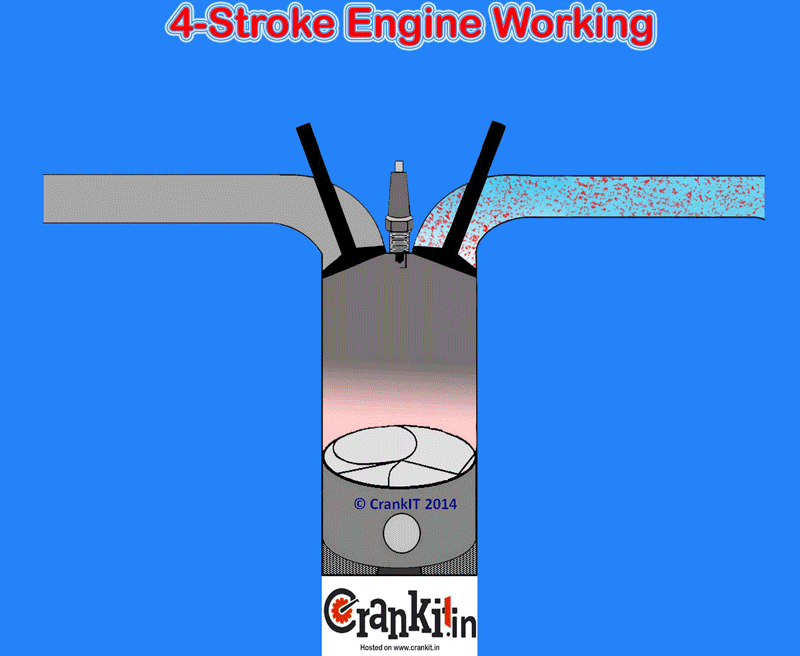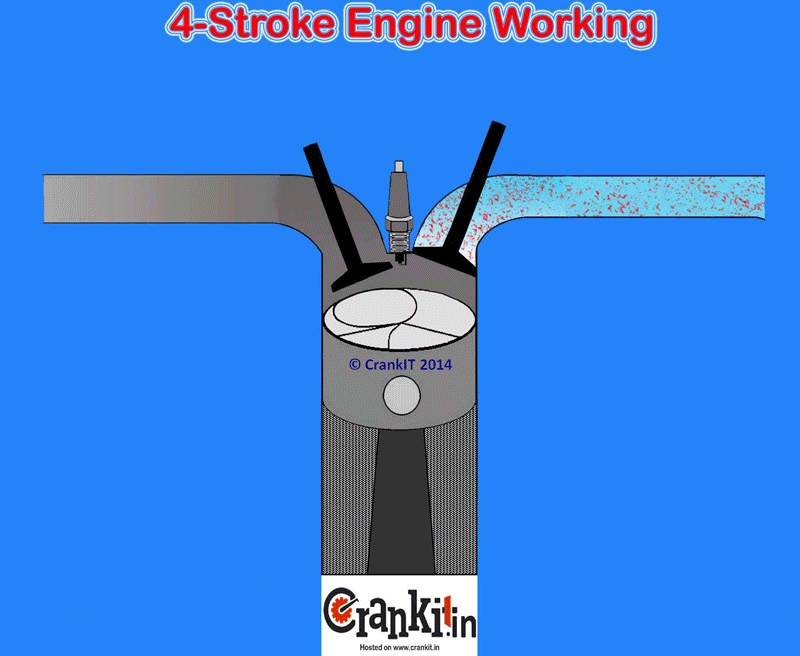
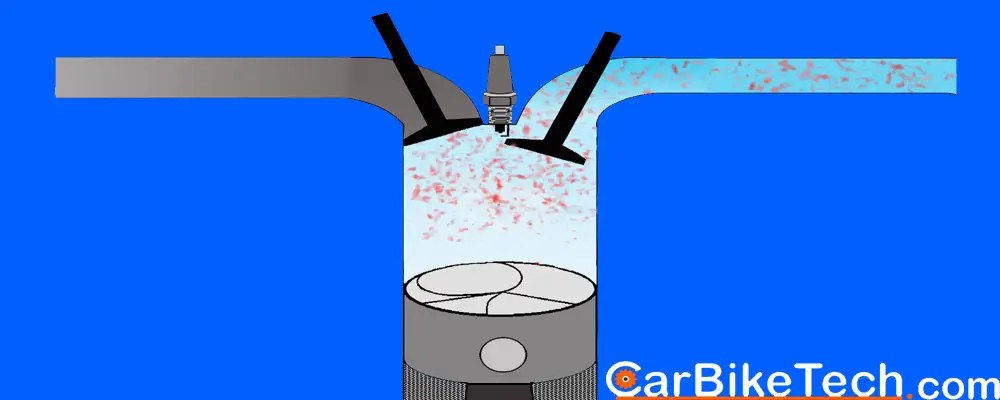
Before diving into the modifications, it’s crucial to understand the basic principles of how an NA engine works. An NA engine relies on atmospheric pressure to draw air into the cylinders. The engine’s performance is therefore heavily dependent on its ability to efficiently breathe – that is, to get air in, burn it effectively, and expel the exhaust gases.
Key Areas for Modification
The following areas are prime targets for modification when aiming to improve the performance of an NA engine:
- Intake System: Improving airflow into the engine.
- Cylinder Head: Optimizing airflow and combustion within the engine.
- Engine Internals: Enhancing engine strength and efficiency.
- Exhaust System: Reducing backpressure and improving exhaust flow.
- Engine Management: Tuning the engine to take full advantage of the modifications.
Detailed Modification Guide
-
Intake System Enhancements:
- Cold Air Intake (CAI): A CAI replaces the factory airbox with a system that draws air from outside the engine bay, where it’s cooler. Cooler air is denser, containing more oxygen, which leads to better combustion.
- Throttle Body Upgrade: A larger throttle body allows more air to enter the engine at full throttle. This is most effective when paired with other intake modifications.
- Intake Manifold: Upgrading the intake manifold can improve airflow distribution to the cylinders. Aftermarket manifolds are often designed with shorter, wider runners to increase airflow at higher RPMs.
- Air Filter: A high-flow air filter (e.g., a cotton gauze filter) offers less restriction than a paper filter, allowing for increased airflow. Ensure proper filtration to protect the engine.
-
Cylinder Head Optimization:
- Porting and Polishing: Porting involves reshaping the intake and exhaust ports in the cylinder head to improve airflow. Polishing reduces friction and promotes smoother airflow. This is best left to experienced professionals.
- Valve Job: A valve job ensures that the valves seal properly against the valve seats, maximizing compression and combustion efficiency.
- Valve Upgrade: Upgrading to larger valves allows for increased airflow into and out of the cylinders. Lightweight valves can also improve engine response.
- Valve Springs and Retainers: Upgrading the valve springs and retainers is essential when installing a more aggressive camshaft. Stronger springs prevent valve float at high RPMs.
- Camshaft Upgrade: The camshaft controls the timing and duration of the valve opening and closing. A more aggressive camshaft can significantly increase power, but it may also affect idle quality and low-end torque. Carefully consider the camshaft profile and its intended use.
-
Engine Internal Upgrades:
- High-Compression Pistons: Increasing the compression ratio can significantly boost power, but it may require higher-octane fuel. Ensure that the engine can handle the increased stress.
- Connecting Rods: Upgrading to stronger connecting rods is essential when increasing power significantly, especially at higher RPMs. Forged connecting rods are stronger and more durable than cast rods.
- Crankshaft: A balanced and lightweight crankshaft can improve engine response and reduce vibration.
- Engine Balancing: Balancing the rotating assembly (crankshaft, connecting rods, and pistons) reduces vibration and allows the engine to rev more freely.
-
Exhaust System Optimization:
- Headers: Aftermarket headers replace the factory exhaust manifold with a system designed to improve exhaust flow. Long-tube headers are generally better for low-end torque, while shorty headers are better for high-RPM power.
- High-Flow Catalytic Converter: A high-flow catalytic converter reduces backpressure while still meeting emissions requirements.
- Cat-Back Exhaust System: A cat-back exhaust system replaces the exhaust system from the catalytic converter back to the tailpipe. It can improve exhaust flow and enhance the exhaust note.
-
Engine Management Tuning:
- ECU Remapping: The engine control unit (ECU) controls various engine parameters, such as fuel injection and ignition timing. Remapping the ECU allows you to optimize these parameters for your specific modifications.
- Standalone Engine Management System: A standalone engine management system replaces the factory ECU and offers greater flexibility and control over engine parameters. This is often necessary for heavily modified engines.
- Fuel Injectors: Upgrading to larger fuel injectors is necessary when increasing power significantly, as the factory injectors may not be able to supply enough fuel.
- Fuel Pump: A higher-flowing fuel pump may be required to supply the larger fuel injectors.
Important Considerations
- Budget: Engine modifications can be expensive. Set a budget and prioritize the modifications that will provide the most significant gains for your money.
- Compatibility: Ensure that the modifications you choose are compatible with your engine and other components.
- Professional Installation: Some modifications, such as porting and polishing the cylinder head or installing a standalone engine management system, are best left to experienced professionals.
- Tuning: Tuning is essential to ensure that your engine runs properly and safely after modifications. Work with a reputable tuner who has experience with your engine.
- Reliability: Keep in mind that modifying an engine can affect its reliability. It’s important to choose high-quality parts and have the work done properly to minimize the risk of problems.
- Emissions: Be aware of local emissions regulations and ensure that your modifications comply with them.
- Research: Thoroughly research each modification before making a purchase. Read reviews, talk to other enthusiasts, and consult with professionals to make informed decisions.
The Value of Incremental Upgrades
It’s often best to approach engine modifications in stages. Start with basic modifications, such as a cold air intake and cat-back exhaust system, and then gradually move on to more advanced modifications. This allows you to see the results of each modification and make adjustments as needed.
The Bottom Line
Modifying a naturally aspirated engine can be a rewarding experience. By carefully planning your modifications and working with experienced professionals, you can unlock hidden potential and enjoy the raw, responsive power of your NA engine. Remember to prioritize reliability and safety, and always tune your engine properly after making modifications.